L03: Computing Concepts
L03: Reflection
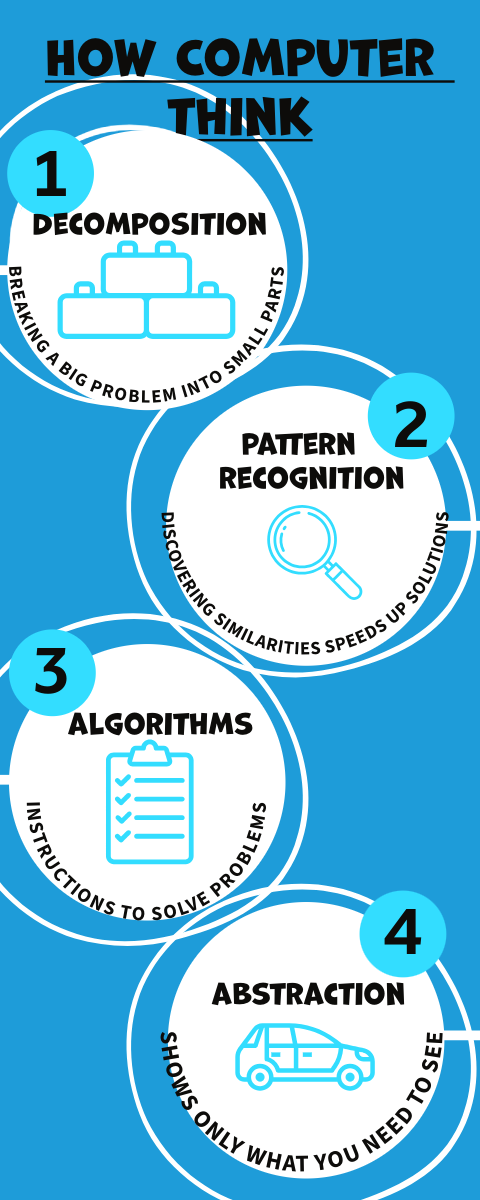
This lesson made me think about how much humans can adapt both physically and mentally to new challenges. Physically,people create tools, machines, and technology to make up for our natural limits. Mentally, we adapt by learning new skills, solving problems, and figuring out better ways to do things. It showed me that a lot of human progress comes from finding ways to work smarter, not just harder. Technology and knowledge let us push past the limits we were bornwith, and that’s what really drives growth and change.
L03: Data Analytics
From the reading within Zybooks what I found most confusing is the word choice for ‘prescriptive’. Overall, though I understand the definitions for all three. For instance, lets say you want to know the number of student who take out student loans and the amount they take out. You would take that data and look for insight within that data like why do the amounts vary. From that data we can make predictions. This is predictive analysis. From those predictions it tells us what should be done to get a specific outcome. That is prescriptive analysis.